For many years, ESA’s ESOC (European Space Operations Centre) has been actively researching how current and future space missions can benefit from Artificial Intelligence (AI), collaborating closely with European AI research institutes, academia, industry partners, and national agencies. In 2021, ESOC initiated a project aimed at outlining a clear direction for AI implementation in mission operations. This initiative led to the creation of the Artificial Intelligence for Automation (A2I) Roadmap, developed by a team of over 70 specialists at ESOC, with support from an industry consortium. The roadmap underwent further validation and refinement in collaboration with the European space and IT sectors.
Mission operations encompass a wide range of tasks, including mission analysis, flight dynamics, operations preparation, simulator development, and satellite and ground station monitoring and planning. The A2I Roadmap team conducted a thorough analysis starting from pain points to evaluate the potential impact of numerous AI use cases in mission operations and space safety, with activities at ESOC serving as a reference point. This analysis included an assessment of the data landscape, technological readiness, and feasibility of each identified use case. The findings indicated that AI can significantly enhance mission operations by streamlining processes, reducing workload, and automating repetitive tasks.
Through strategic collaboration and focused development, the A2I Roadmap pinpointed 14 specific use cases across five priority mission operations domains for targeted AI application development. By capitalizing on synergies to facilitate cross-development, minimize deployment time, and enable scalability, the roadmap aims to maximize the effectiveness of AI integration in mission operations.
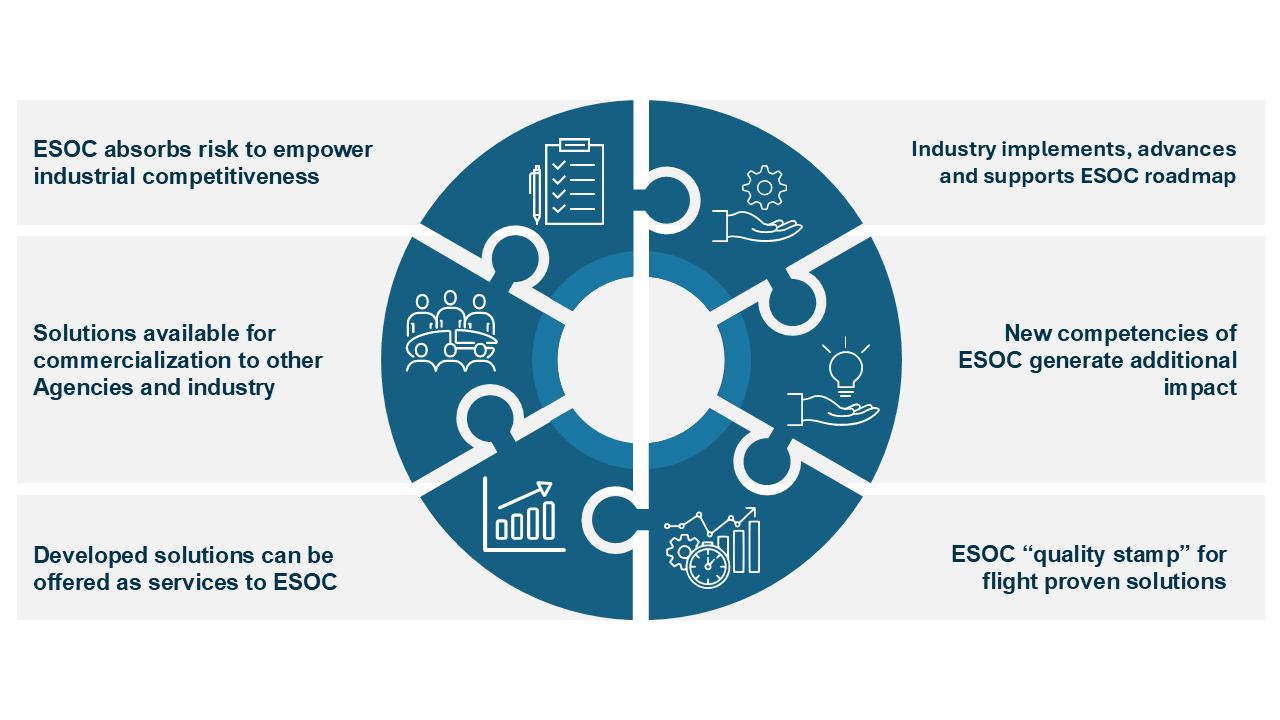
The main objective of the A²I Roadmap is to cultivate the growth of the European Space Sector by leveraging applied AI in mission operations. Alongside this goal, the roadmap presents various supplementary advantages, illustrated in the infographic below. Furthermore, it guarantees ESA’s continued prominence in both advancing and implementing AI for spacecraft mission operations, solidifying its role as a primary facilitator for the European industry, reinforcing ESA’s Agenda 2025 artificial intelligence aspirations and ESA ongoing transformation.
Data Foundation Target State and Execution Plan
ESOC and European Mission Operations Centres manage various diverse missions, each of which presents different needs in the daily generation, collection, storage and distribution of their data. The data is commonly processed and stored in separate, siloed systems.
While this current decentralised architecture has proven efficient for managing complex operations and ensuring reliable data delivery, it poses several challenges for data users, such as scientists, engineers, and AI systems. They often struggle to access, analyse and interpret the large volumes of structured and unstructured data due to difficulties in integrating data from various data sources, suboptimal access controls and the limitations of scaling on-prem systems. This fragmented nature of the data architecture and governance complicates advanced analytics including AI applications, as traditional systems are ill-suited to handle the volume, velocity, and variety of data generated in modern space operations.
ESOC aims to enhance the scalability of advanced analytics applications by implementing best practices for managing data and analytics products as valuable, reusable assets. This approach increases their value within the organisation and democratises data access, both internally and externally, thus also enabling industrial use cases. In the process of determining the most effective design of a common data layer, a comprehensive analysis of ESOC’s data and system landscape was conducted. This included exploring various approaches and architectures, such as various data platform architecture archetypes and cloud-native features. The investigation highlighted three key areas of focus in order to streamline the systematic production of data products: data architecture, data governance and data management.
The architecture for the common data layer was then designed to accommodate a wide range of data types and formats, from structured data in databases to unstructured data in files and streams. The system includes tools for data ingestion, processing, storage and analytics, ensuring comprehensive data management. Additionally, data governance strategies were outlined to maintain data quality, consistency, and security.
Implementation
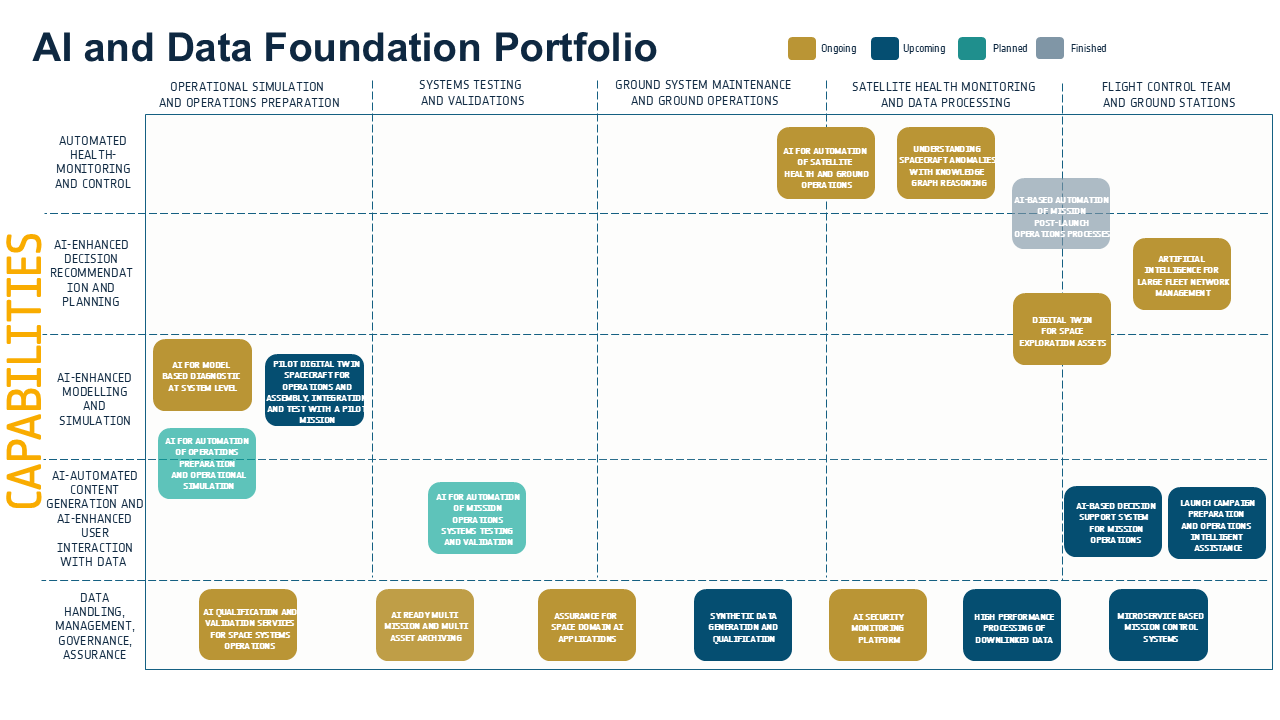
At ESOC, several AI initiatives beyond the primary use cases of the A2I Roadmap are under development to advance the technology across readiness levels (TRLs) and address the foundational data layer and machine-learning processes supporting all AI applications. By assimilating and incorporating cutting-edge methodologies, ESOC will continue to lead in mission operations, fostering future innovation, democratizing access to data, and enhancing efficiency. The A2I Roadmap hence became an input to the “AI and Data Foundation Project” (AiDAPT) for mission operations. It focuses on generating five capabilities.
- Automated system health monitoring and control: this capability allows AI-enhanced detection of anomalous conditions, diagnostics, prognostics and automates processes with the monitoring and control of spacecraft and ground segment.
- AI-enhanced decision recommendation and planning: this capability allows for mission planning, scheduling, and decision-making enhanced by AI.
- AI-enhanced modelling and simulation: this capability provides AI-enhanced simulation engines to be integrated into operational simulators. It enhances mission-critical analyses, simulations fidelity and representativeness, situational awareness, calibration synchronization of simulators and supports system health monitoring and decision making.
- AI-automated content generation and AI-enhanced user interaction with data: the capability allows the use of AI to support generating reports and analyses, and exploring data with user-friendly interfaces.
- Data handling, data management, data governance, data assurance: the capability provides structured data, improves user interfaces, enhances data systems and architectures and provides pipelines for governance and assurance.
AI and Data Foundation for Missions Operations
The present array of AI technology development endeavours is illustrated in the accompanying infographic. Applications are categorized by domain and capability, with data foundation activities serving as the foundational layer across all applications, functioning as a pervasive enabler. Purely research collaborations with European research institutes and universities are not included in this depiction.
Journey
ESOC is collaborating with European industry, research institutes, and national agencies to implement AiDAPT. Beyond the technical aspects, a crucial focus entails addressing the human dimension to ensure the adoption and acceptance of developed solutions. This is accomplished through a user-centric approach, focusing on user experience, and agile methodologies, where cross-functional teams from ESA and industry work closely together, conducting daily check-ins and fortnightly sprint reviews and planning sessions. The management of these agile activities follows principles of “Agile at scale”, including periodic coordination meetings across all involved activities.
Since publishing the A²I Roadmap in 2021, several notable results and solutions are being developed. Among these, the following stand out:
- AInabler. ESOC, in collaboration with industry partners, has developed AInabler, aimed at facilitating the structured and scalable deployment of accessible AI applications. Inspired by MLOps principles, this platform empowers users to construct, train, and implement machine learning models for automating space operations. Providing a platform-as-a-service that can be deployed as required, AInabler is available to internal ESOC projects and ESA affiliates, contractors, and third-party collaborators driving data and software developments. AInabler supports advancing Capability #5. For documentation and source code of the AInabler platform, visit the dedicated website: https://ainabler.space-codev.org/.
- OCAI. The Operations CompAnIon (OCAI) is an AI tool designed to enhance decision-making processes for flight control teams. With the growing complexity of systems and data fragmentation, virtual assistants are increasingly valuable. ESOC has addressed this need by developing OCAI, which streamlines data retrieval, correlation, and analysis across multiple heterogeneous systems. Its core capabilities include advanced search and data correlation across diverse sources, supporting concise open language queries including Mission Operations specific terminology. OCAI has already demonstrated to enhance operational efficiency for 10 missions. The upcoming developments will cover higher semantic search capabilities, human language interaction and content generation leveraging primarily the high potential of Generative AI. OCAI supports advancing Capability #4. For documentation and source code of the Ops Companion, visit the dedicated website: https://ocai.space-codev.org/
- 4caster. A short-term time-series forecasting application that leverages an AI foundation model to describe spacecraft’s telemetry parameters behaviour. It is fully integrated into the existing ESOC technology stack to facilitate adoption by end users. Developed and operationalized on one ESA mission, plan to make it used in operations and extend its use to other ESA missions is being finalized. 4caster supports advancing Capability #1.
- Root-cause anomaly assistant. A large language model (LLM)-powered application to assist in root-cause investigation of anomalies by retrieving and consolidating relevant information, previously performed manually by flight control teams. Developed and operationalized on two ESA missions, the roll out plan to extend its use to other missions is under refinement. This application supports advancing Capability #1.
- ESA Anomaly Dataset. The first large-scale, real-life satellite telemetry dataset with curated anomaly annotations originated from three ESA missions. It was released to the public on Zenodo in June 2024 to benchmark models and approaches on a common baseline as well as stimulate research and develop novel, computational-efficient approaches for anomaly detection in satellite telemetry data. The ESA Anomaly Dataset supports advancing Capability #1.
For every application developed, we also measure impact. So far, this has demonstrated that the original business case we produced was conservative, and benefits extend well beyond the metrics initially considered.
Our plan foresees completing the original A2I Roadmap in 2025. Development is on time and well underway. For the application layer, one GSTP (General Support Technology Programme) activity was completed and two are under implementation. The Data Foundation execution plan includes multiple activities that were awarded and begun implementation recently.
Selected publications and references
- DataX: a state-of-the-art data strategy for mission operations. International Astronautical Congress 2024 (to be published), 2024
- Constellation Autonomy: AI solutions for adaptable and efficient operations. International Astronautical Congress 2024 (to be published), 2024
- Smart Space Operations: OCAI's contribution to Operational Excellence. International Astronautical Congress 2024 (to be published), 2024
- Artificial intelligence-based automation of mission post-launch operations processes. International Astronautical Congress 2024 (to be published), 2024
- Intelligent root-cause investigation and AI-assisted handling tool for flight control teams. International Astronautical Congress 2024 (to be published), 2024
- Artificial Intelligence-based short-term satellite health forecasting. International Astronautical Congress 2024 (to be published), 2024
- Automation of flight dynamics planning for ESA's XMM- Newton. International Astronautical Congress 2024 (to be published), 2024
- European Space Operations unified Knowledge Base Natural Language Interface. 2024 SPAICE, 2024
- European Space Agency Benchmark for Anomaly Detection in Satellite Telemetry. arXiv, 2024
- ESA Anomaly Dataset (1.0). Zenodo, 2024
- AI-based decision support system for mission operations. European Space Agency, 2024
- AI qualification and validation services for space systems operations. European Space Agency, 2023
- Assurance for space domain AI applications. European Space Agency, 2023
- AI-ready multi mission and multi asset archiving. European Space Agency, 2023
- AI for automation of satellite health monitoring and ground operations. European Space Agency, 2023
- Development of an actionable AI roadmap for automating mission operations. 2023 SpaceOps Conference, 303, 2023
- OCAI: the Operations CompAnIon to support decision making of flight control teams. 2023 SpaceOps Conference, 2023
- ESTIM: the ESTrack Investigation and Monitoring tool for analysis of ground station passes. 2023 SpaceOps Conference, 2023
- Towards an AI-enhanced robotic digital twin for space exploration assets. 2023 SpaceOps Conference, 2023
- Space debris streak classification: a transparent deep learning approach to reduce false positive detections. 2023 SpaceOps Conference, 2023
- Artificial intelligence based automation of mission post-launch operations processes. European Space Agency, 2022
- Sunspot groups detection and classification on SDO/HMI images using deep learning techniques. IEEE Aerospace Conference, 2022
- Intelligent Operations and Preventative Maintenance Assistant. European Space Agency, 2021